Call our friendly podiatrists today on (08) 9586 3046
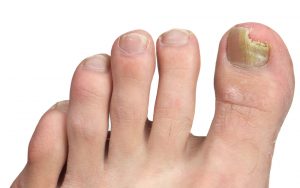 Fungal infections of the foot can affect the toenails and the skin.
Fungal infections of the foot can affect the toenails and the skin.
Fungal infection is the most common disease of the nails and constitutes about half of all nail abnormalities. Toenails are affected more commonly than fingernails and approximately 6-8 percent of the adult population is affected by this condition. Men are more often affected than women and usually later in life, after the age of 40.
Signs of fungal toenail infection include nails that are discoloured (white or yellow), brittle, crumbly or ragged, thickened, distorted in shape and separated from the nail bed. There is usually no pain or other bodily symptoms, unless the disease is severe.
Risk factors for toenail fungal infection include family history, increasing age, poor health, poor foot hygiene , prior trauma to the nails, warm, damp climate, participation in fitness activities which can lead to repeated minor trauma, diseases that influence the immune system (e.g. HIV, diabetes), exposure to damp communal areas (e.g., gyms, swimming pools), , and occlusive footwear.
Prevention
Fungal nail infection can be effective treated with Lunula laser therapy.
Lunula is the latest and most revolutionary medical laser technology that is highly effective at resolving fungal nail infection. Safe and effective, Lunula Laser is the first and only non-thermal laser to receive FDA 510(k) Market Clearance for Onychomycosis
Lunula Laser therapy has an amazing 89% success rate!
The Lunula delivers a combination of two lasers simultaneously at very specific wavelengths to the surface of your feet. The lasers generate a rotating beam and can cover a large area of the foot to completely treat infections within the nails and nail bed. The two lasers used in the Lunula are:
Blue (405nm), this acts directly and specifically upon the fungus and causes changes in its outer wall, this weakens it significantly, allowing the body’s immune system to attack and destroy it.
Red (635nm), is acting upon the body’s natural immune cells – fortifying them, thus making them more active and able to neutralize and destroy the weakened fungus. In addition the red light can stimulate and improve blood flow; this additional blood flow brings nutrients and additional immune cells to the affected area speeding up the treatment process.
The treatment will last for 12 minutes and is pain free, the lasers are not harmful to you in any way as they use very low power settings.
Please click here for more information